Ischemic Stroke and Carotid Artery Disease

Therapies
This portfolio includes carotid stents, aspiration catheters and mechanical thrombectomy products


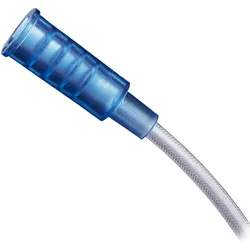
SOFIA™ Flow Plus
Aspiration Catheter
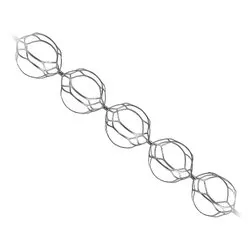
ERIC™
Retrieval Device
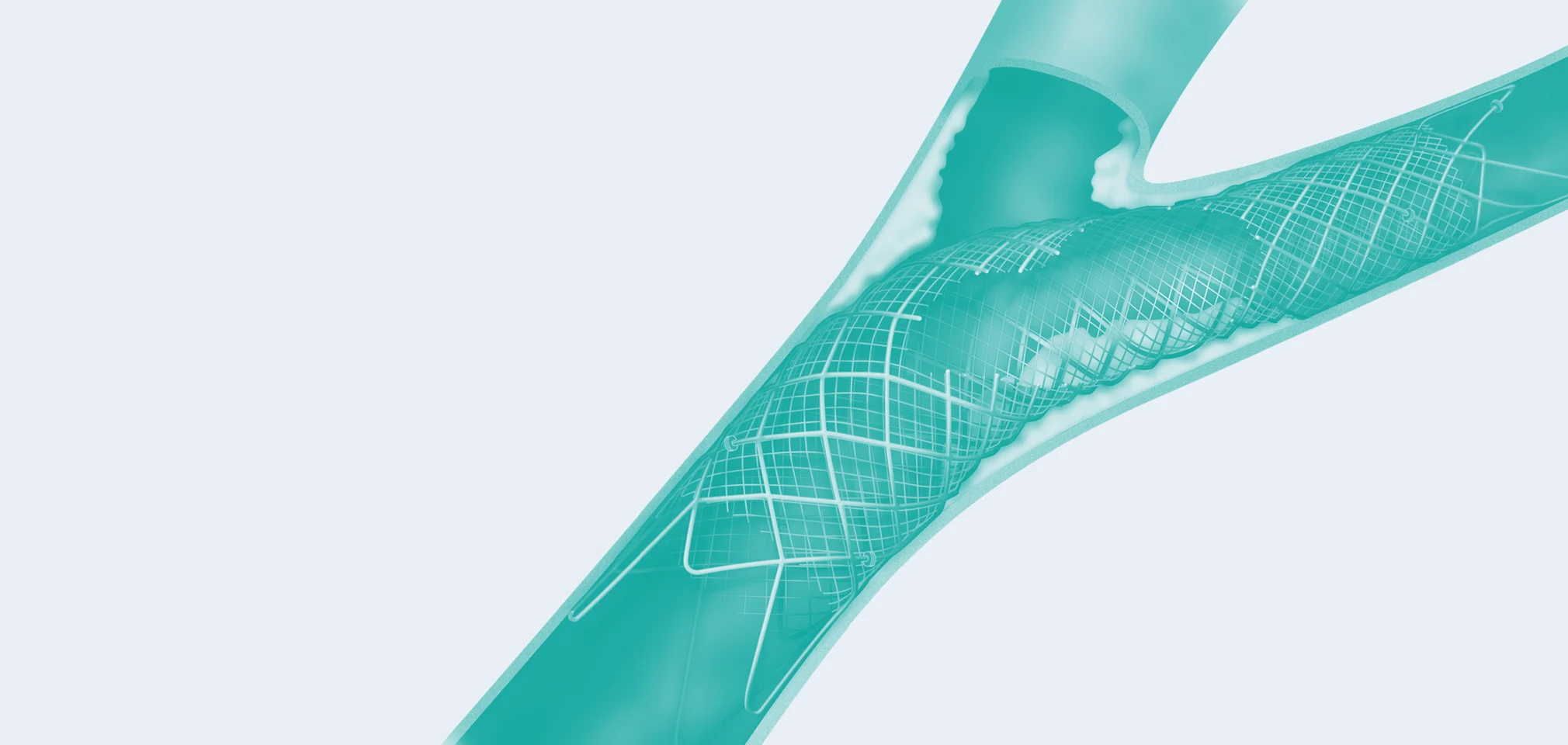
02 — Carotid Stenting
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) is an endovascular procedure where a stent is deployed within the lumen of the carotid artery to treat narrowing of the carotid artery and decrease the risk of stroke.
No devices approved in this region.