Aneurysm Therapy

Therapies
MicroVention provides a full range of neuro-interventional products to treat brain aneurysms


HydroFrame™
Hydrogel Embolic Coils

HydroSoft™ 3D & HydroSoft™ Helical
Hydrogel Embolic Coils

Cosmos™
Platinum Coils

HyperSoft™ 3D & HyperSoft™ Helical
Platinum Coils
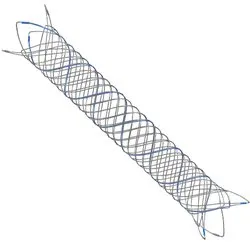
LVIS™ & LVIS™ Jr
Coil Assist Stents


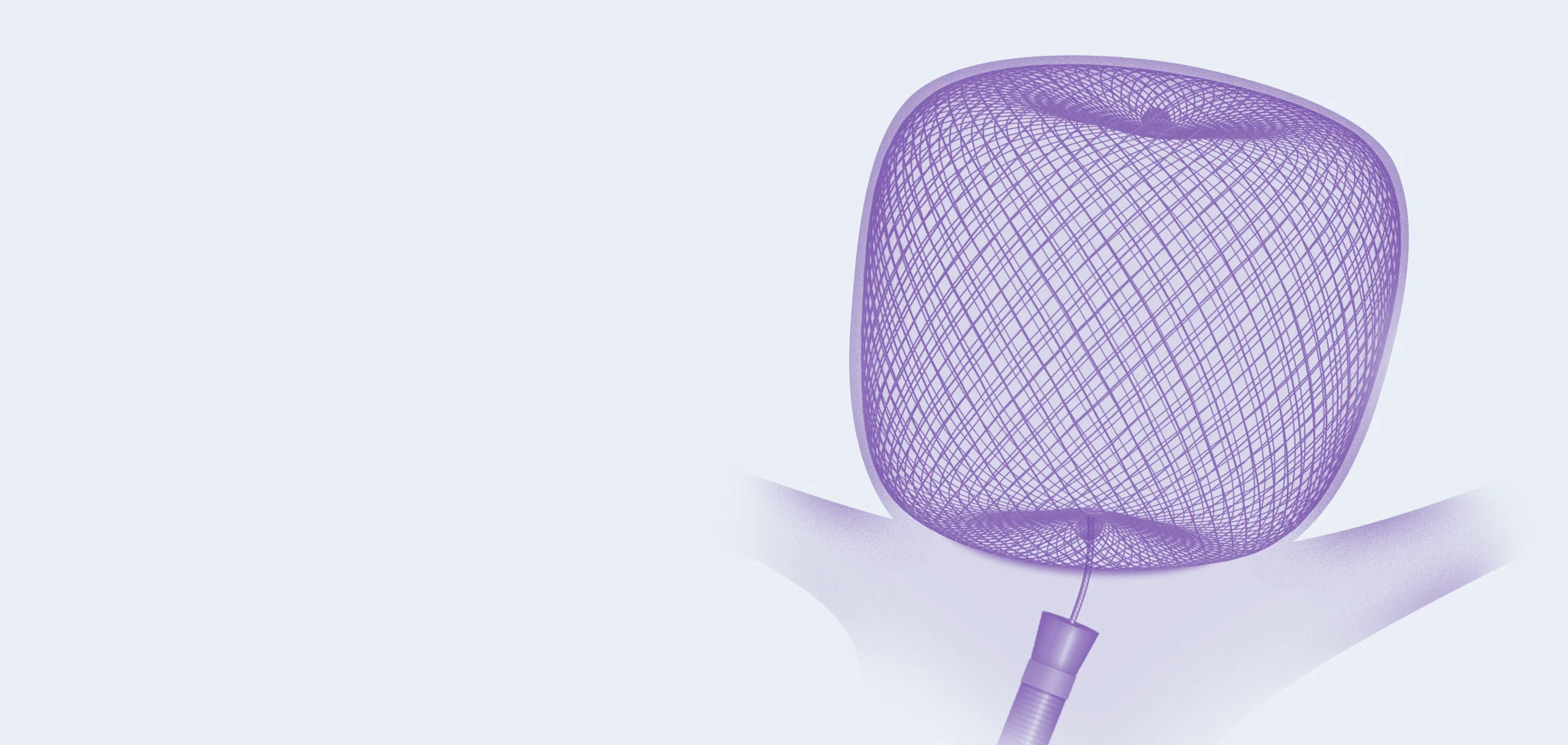
WEB™ Embolization System
Intrasaccular Devices
03 — Flow Diversion
The Flow Diversion technique uses a low porosity stent across a wide-necked brain aneurysm. The device is placed across the aneurysm neck opening, and extends into the parent artery on both sides. This alters intra-aneurysmal blood flow patterns and redirects flow away from the aneurysm
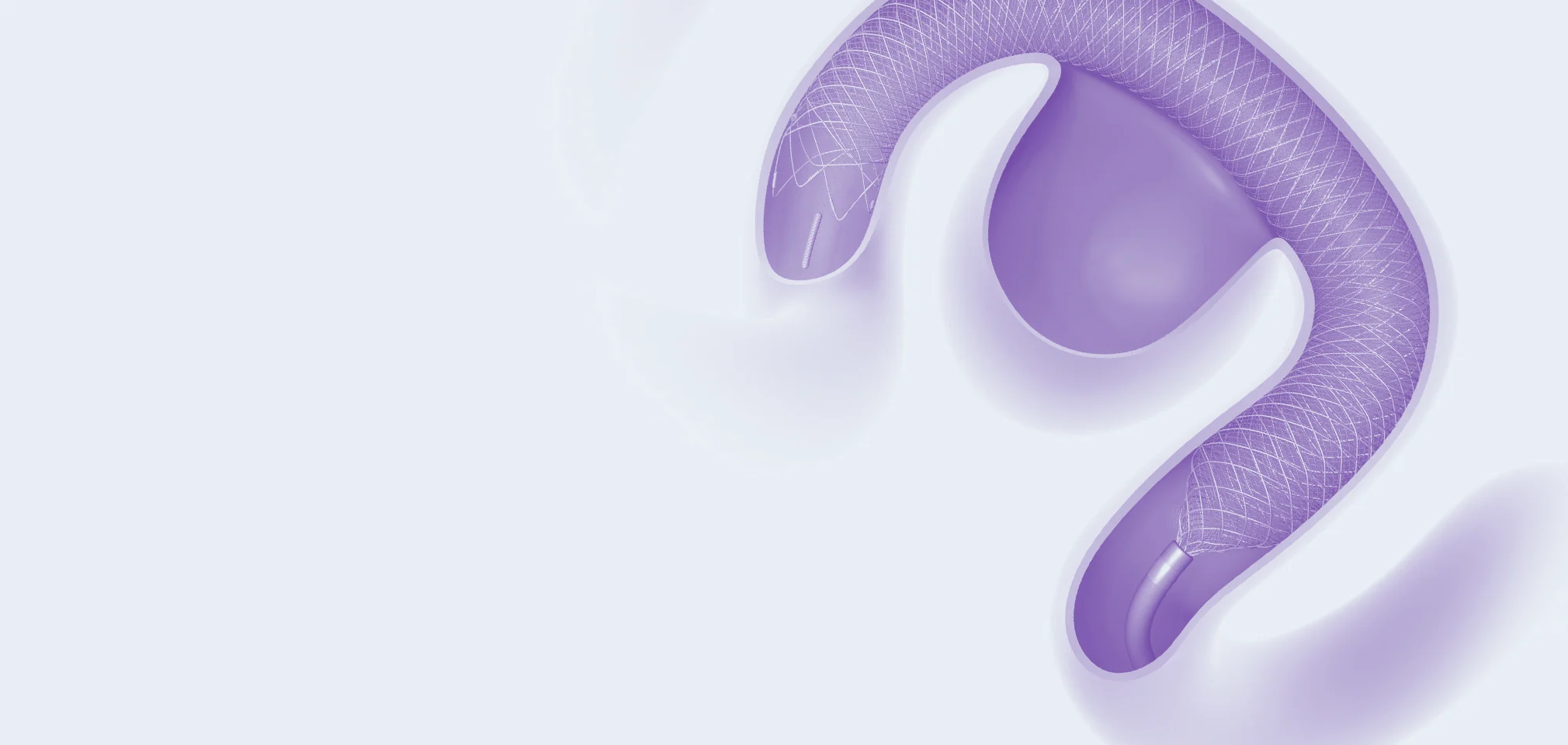


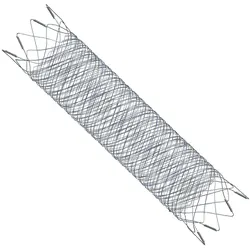
FRED™
Flow Diverter
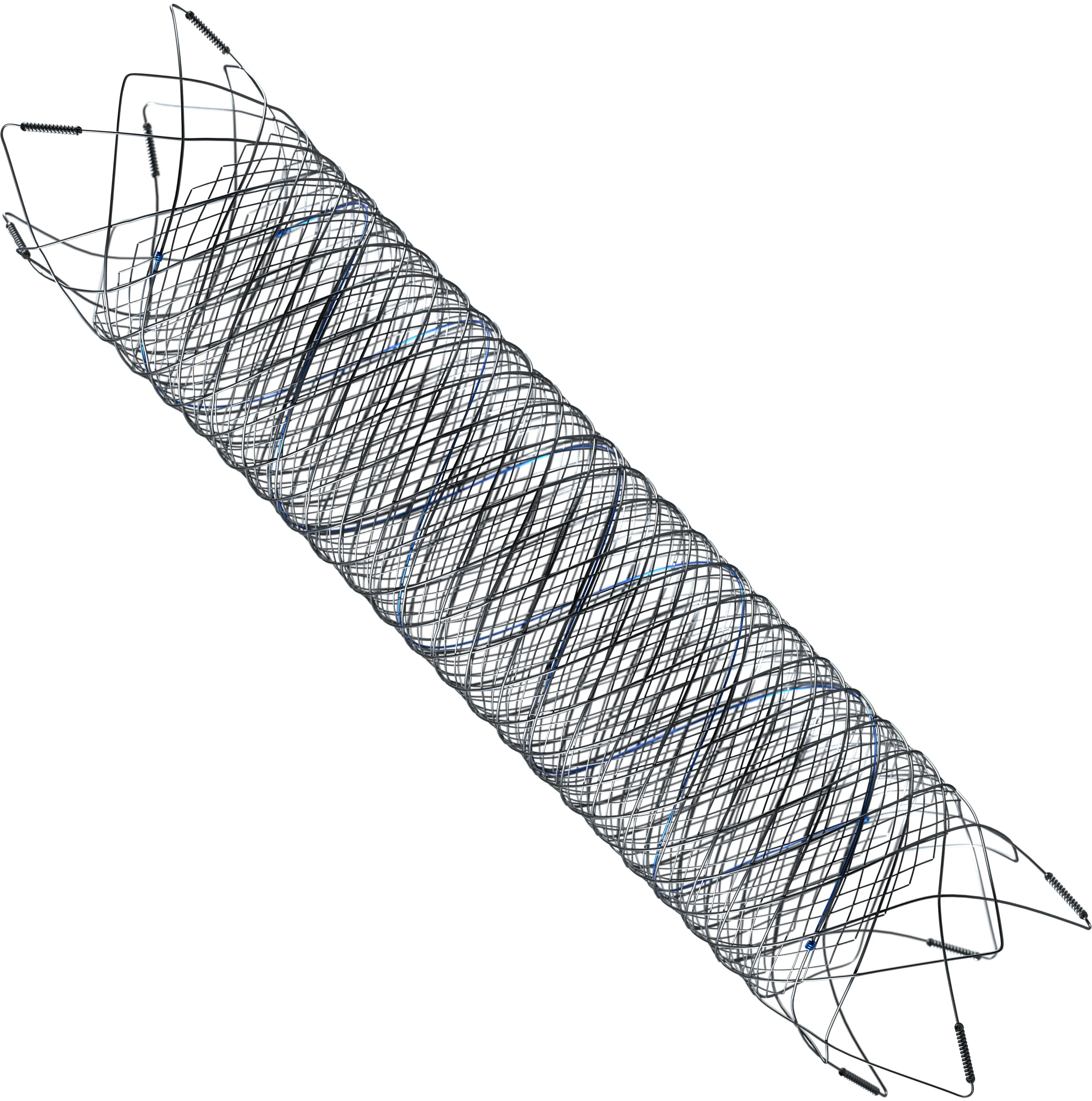
FRED™ X
The Next Advancement in Flow Diversion Technology





